IPTV channel zapping time¶
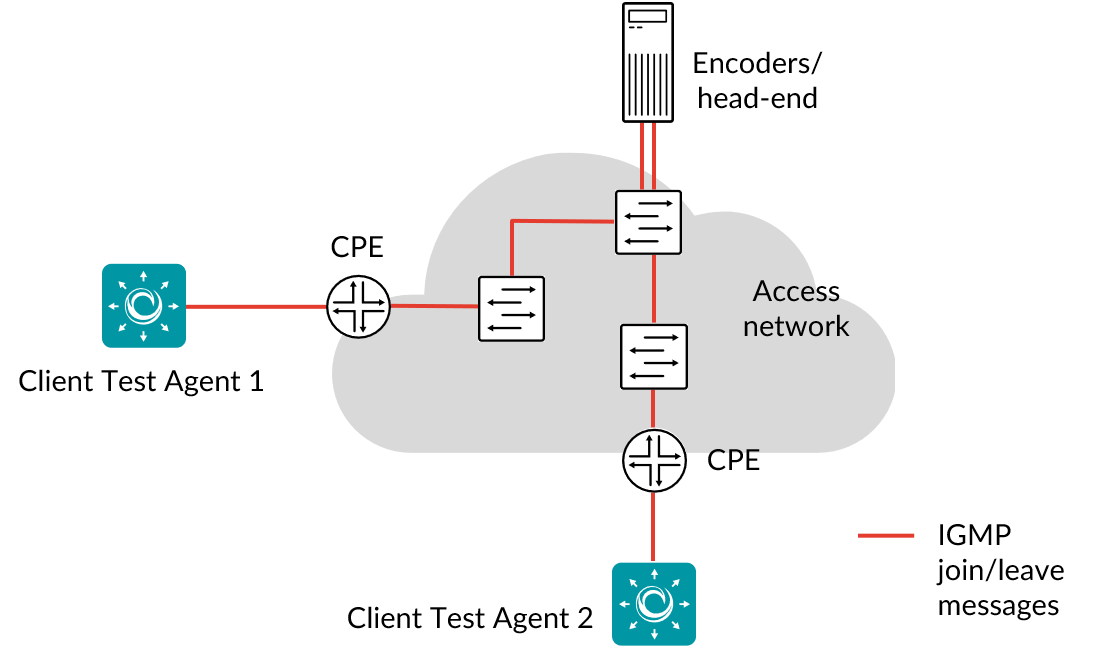
This task measures zapping times (in ms) when switching between different IPTV channels. An IPTV channel zapping consists of two IGMP messages: an IGMP join and an IGMP leave.
The IPTV channel zapping task lets you monitor and test channel change times, that is, how long it takes from the customer switching channels until the new channel is received.
When this task starts, the Test Agent starts zapping between the selected multicast channels. It waits a specified length of time for each zapping to complete (i.e. to receive traffic on the new channel). At the end of the task, the Test Agent reports the minimum, maximum, and average zapping times (the maximum will be limited to the timeout setting).
Prerequisites¶
To run IPTV channel zapping measurements you need to have at least one Test Agent installed. If you haven’t already done the installation, consult the installation guides found here.
Also make sure that you have prepared Routing Active Testing with your IPTV channel list.
Note
Please note that it does not make sense to run an IPTV channel zapping task on a channel where the same Test Agent is already running an IPTV monitoring session on the same interface. (If this is the case, the Test Agent will not leave the channel on IGMP leave, since the IPTV monitor stipulates that the channel should be received continuously. In other words, because of the way multicast works, the IPTV monitor will interfere with the IPTV channel zapping.)
In your test or monitor, add an IPTV channel zapping time task and fill in the mandatory parameters below:
This task works with both IPv4 and IPv6.
Parameters¶
See the common parameters page for the following:
Parameters that are set on the test step level: Duration, Fail threshold, and Wait for ready.
SLA thresholds for monitors: SLA Good and SLA Acceptable.
Advanced settings common to all test tasks: Delayed start.
General¶
Clients: Test Agent interfaces to use as clients.
Channels: IPTV channels to monitor from the preset IPTV channel list.
See this page.Min wait time between zapping: The minimum time a client will wait between consecutive zappings.
Each zapping is constituted by an IGMP join and an IGMP leave message. Min: 0 ms. Default: 2000 ms.Max wait time between zapping: The maximum time a client will wait between consecutive zappings.
Min: 0 ms. Default: 2000 ms.
Note
If you set Min wait time… and Max wait time… differently, the wait time between zappings will be randomized within the specified interval.
Thresholds for errored seconds (ES)¶
Threshold for join delay: The join delay is the time from when the client issues an IGMP join message for a multicast group until the first packet is received for that multicast group. An errored second is triggered if this threshold is exceeded.
The default value is set to 500 ms in accordance with ► ETSI TS 102 034 (2009-08). Min: 0 ms. Default: 500 ms.Threshold for leave delay: The leave delay is the time from when the client issues an IGMP leave message for a multicast group until the last packet is received for that multicast group. An errored second is triggered if this threshold is exceeded.
The default value is set to 500 ms in accordance with ETSI TS 102 034 (2009-08). Min: 0 ms. Default: 500 ms.
Result metrics¶
Average join delay (ms): Average delay from sending an IGMP join until the flow arrived.
Minimum join delay (ms): Minimum delay from sending an IGMP join until the flow arrived.
Maximum join delay (ms): Maximum delay from sending an IGMP join until the flow arrived.
Failed joins: Number of failed IGMP joins. A join fails if the flow does not arrive before an IGMP leave is sent.
Average leave delay (ms): Average delay from sending an IGMP leave until the flow was stopped.
Minimum leave delay (ms): Minimum delay from sending an IGMP leave until the flow was stopped.
Maximum leave delay (ms): Maximum delay from sending an IGMP leave until the flow was stopped.
Failed leaves: Number of failed IGMP leaves. A leave fails if the flow is not stopped before a new IGMP join is sent.
ES join: Number of errored seconds triggered by a failed IGMP join occurring during the second.
ES leave: Number of errored seconds triggered by a failed IGMP leave occurring during the second.
ES total: Aggregated errored second percentage, taking into account all types of error.
SLA: Service level agreement fulfillment: equal to (100 – ES total) %.