IPTV MPEG inline¶
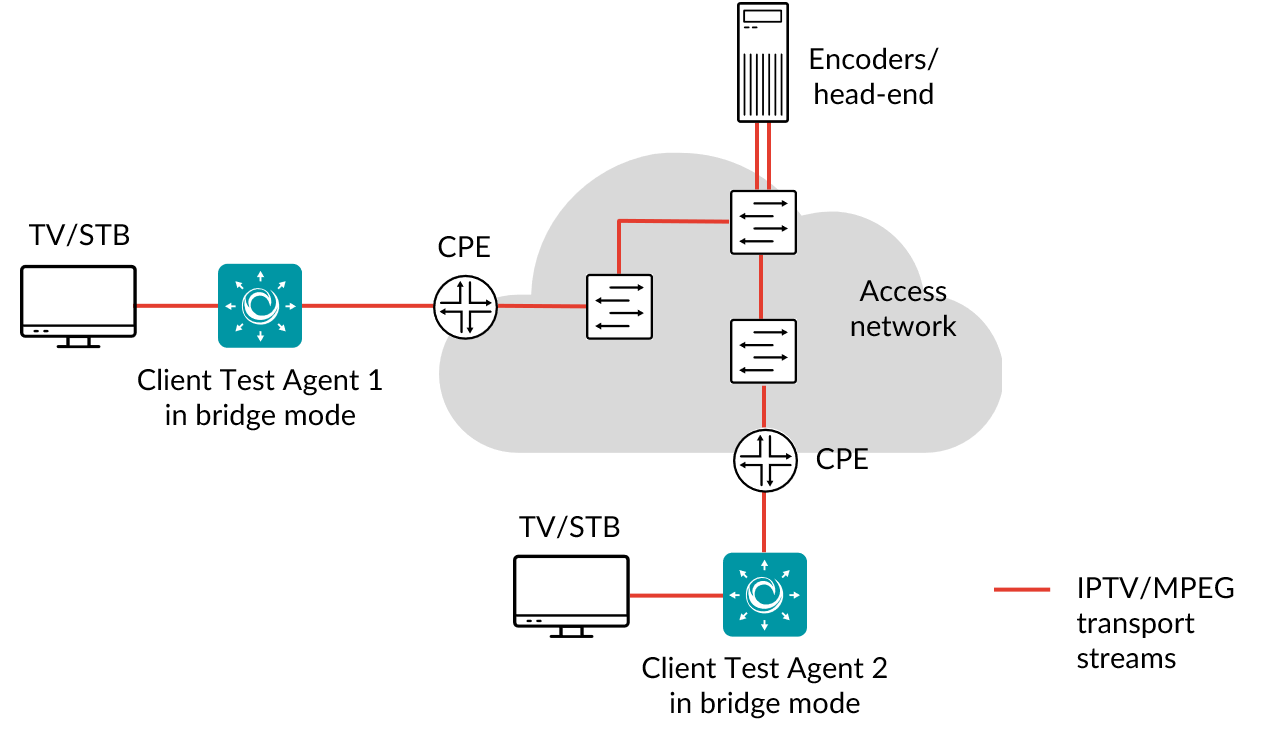
The IPTV MPEG inline task lets you monitor the quality of TV channels that customers are watching. When this task starts, Routing Active Testing will start listening to the IGMP signaling (IGMPv2 is supported, whereas IGMPv3 is not) and measure on the channels that the set-top box joins. Measurements include MPEG loss, PCR jitter and data rate; Routing Active Testing will also alert you about any general problems with the MPEG stream.
Note
Routing Active Testing will only measure on channels that are on its preconfigured IPTV channel list (see this page). If a set-top box joins a channel that is not present in the Routing Active Testing channel list, no measurement data will be obtained. Note also that Routing Active Testing does not decrypt any of the MPEG streams, but utilizes only the unencrypted MPEG headers for quality measurements.
It is possible to configure a threshold for the IPTV PAT/PMT receive interval, that is, define how frequently PAT and PMT information should be detected in the received MPEG stream. Note that this overrides the default frequency of two PAT/PMT packets per second, as specified in ► ETSI TR 101 290 (Measurement guidelines for DVB systems).
Prerequisites¶
To do IPTV inline measurements you need to have at least one Test Agent installed. If you haven’t already done the installation, consult the installation guides found here.
To prepare for IPTV inline measurements, first create a bridge interface and connect it between the residential gateway (CPE) and the customer set-top box (STB).
Also, as noted above, make sure that you have configured Routing Active Testing with your IPTV channel list.
Then add an IPTV MPEG inline task to your test or monitor and fill in the mandatory parameters below:
Parameters¶
See the common parameters page for the following:
Parameters that are set on the test step level: Duration, Fail threshold, and Wait for ready.
SLA thresholds for monitors: SLA Good and SLA Acceptable.
Advanced settings common to all test tasks: Delayed start.
General¶
Clients: Test Agent interfaces on which to receive IPTV channels.
Note: As remarked above, a prerequisite for this task is that the Test Agents have a bridge interface.
Thresholds for errored seconds (ES)¶
MPEG loss (CC errors/s): Maximum tolerated MPEG packet loss (CC errors) per second.
See this page. Min: 0 packets per second. Default: 2 packets per second.Jitter: Maximum tolerated PCR and RTP jitter (delay variation) in the received MPEG streams.
See this page. Min: 0 ms. Default: 50 ms.PAT/PMT interval (s): Maximum tolerated interval between PAT/PMT transmissions.
Min: 0.5 s. Max: 60 s. Default: 0.5 s. Note: PAT/PMT should be received every half-second on a program according to the standards.PID interval (s): Maximum tolerated interval between audio or video PIDs as specified by PMT.
Min: 1 s. Max: 60 s. Default: 5 s. Note: On regular audio/video streams, a PID should be received every 5 seconds according to the standards.
Result metrics¶
Rate (Mbit/s): The bit rate of the MPEG program stream.
Transport rate (Mbit/s): The bit rate of the MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS), that is, the rate of the MPEG stream including the overhead from the header of the Transport Stream packet. See this page for further details.
MPEG loss: MPEG packet loss, calculated from the Continuity_count_error counter in the MPEG stream. See this page.
PCR jitter (ms): The jitter (delay variation) of the received MPEG stream. Calculated from the timestamps in the Program Clock Reference (PCR) field transmitted in the adaption layer of the MPEG transport stream.
RTP jitter, RTP loss, RTP misorders: If the MPEG stream contains RTP headers, Routing Active Testing will calculate RTP jitter, loss, and misorderings, which are basically the same as the corresponding metrics for IP. Whether or not the MPEG stream contains RTP headers depends on the encoder at the head-end.
PAT errors: A PAT error is triggered if a Program Allocation Table (PAT) is not received on a multicast group within PAT/PMT interval.
PMT errors: A PMT error is triggered if a Program Map Table (PMT) is not received on a multicast group within PAT/PMT interval.
PID errors: On regular audio/video streams, a frame should be received in every PID interval. If no frame is received within that interval, one PID error is generated for every second that elapses.
ES MPEG loss: Number of errored seconds triggered by MPEG loss exceeding the MPEG loss threshold during one second.
ES jitter: Number of errored seconds triggered by PCR jitter or RTP jitter exceeding the Jitter threshold.
ES invalid stream: An aggregate of PAT, PMT, and PID errors. If any of these types of error is encountered during a second, it is marked as an “Invalid stream” errored second.
ES total: Aggregated errored second percentage, taking into account all types of error.
SLA: Service level agreement fulfillment: equal to (100 – ES total) %.