Junos TWAMP¶
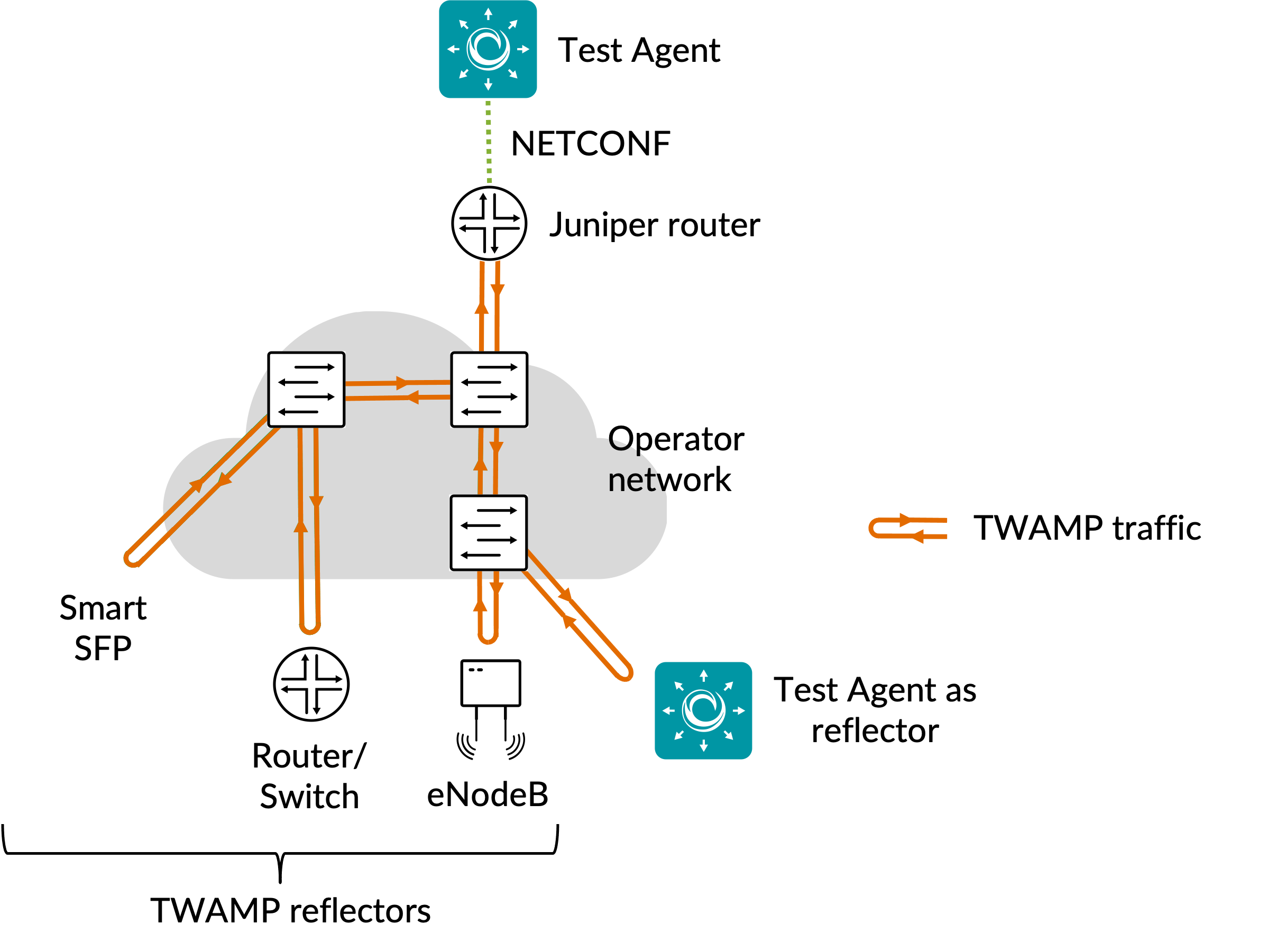
In this task, a Test Agent Application connects to one or several Junos devices (defined as network devices in Routing Active Testing) via the NETCONF protocol and accesses TWAMP sessions running on these devices (these sessions have not been configured in Routing Active Testing). The Test Agent collects measurement results from the TWAMP sessions, evaluates errored second thresholds, and reports all results back to Control Center.
The TWAMP sessions running on the Junos devices are identified based on their configured “control connection” and “test session” (specified as services rpm twamp client control-connection <control connection> test-session <test session> in the Junos CLI). The names of the control connections and test sessions are shown along with the results in Control Center so that you can correlate them with the TWAMP sessions on the Junos device.
TWAMP sessions can optionally be run against other Test Agents acting as reflectors. Such Test Agents then need to be running a TWAMP Reflector task.
Note
A Test Agent Application is required for this task; the Test Agent Appliance does not support it. The Junos TWAMP task is also different from the other TWAMP tasks in that the Test Agent does not itself conduct the measurements.
IPv6 is supported in the communication between the Test Agent and the Junos device. For the communication between TWAMP sender/client and reflector, Junos currently only supports IPv4.
Prerequisites¶
To perform Junos TWAMP measurements, you need to install at least one Test Agent. For guidance on how to deploy a new Test Agent, see the installation guides found here.
As regards each targeted Junos device, the following holds:
The functionality has been verified to work on the following Juniper device models, but it might also work on other TWAMP-capable devices:
vMX
MX204
MX480
MX960
The functionality has been verified for Junos versions 18.3–20.2.
There must be network connectivity from the Test Agent to the device (default TCP port: 830).
You must have a user account on the device to be able to log in to it and retrieve measurement data. How to create a user account is described here.
The Junos device must be configured as a network device in the Routing Active Testing inventory.
The Junos device must be running TWAMP measurements when you execute the Junos TWAMP task. The relevant Junos documentation is found here.
Once you have finished the above preparations, you can add a Junos TWAMP task to your test or monitor and fill in the mandatory parameters as shown below.
Junos device configuration¶
This section is about suitable configuration of the Junos device. This needs to be done directly on the device and cannot be performed in the Routing Active Testing task. For details, please refer to Junos device documentation.
Creating a user account on a Junos device¶
The user account should have limited permissions and can be created as follows:
configure
set system login user <username> class read-only
set system login user <username> authentication plain-text-password
New password: <password>
commit
Configuring TWAMP history size¶
The configuration parameter services rpm twamp client control-connection <control connection> history-size in the Junos device specifies how many historical probe results are stored for each control connection and test session. (Regarding these concepts, see the introductory section above.)
The Test Agent will fetch new probe results from this result set every 5 seconds. To have some margin for communication delays between the Test Agent and the Junos device, we recommend that you configure history-size to correspond to at least 1 minute. For example, with probe-interval set to 10 seconds, we recommend a history-size of at least 6.
Parameters¶
See the common parameters page for the following:
Parameters that are set on the test step level: Duration, Fail threshold, and Wait for ready.
SLA thresholds for monitors: SLA Good and SLA Acceptable.
Advanced settings common to all test tasks: Delayed start.
General¶
Client: Test Agent interface that will connect to the Junos device.
Network devices: Junos devices that are running TWAMP tasks and will be accessed by the Test Agent.
Thresholds for errored seconds (ES)¶
RTT threshold (ms): Round-trip time threshold for triggering an errored second. If the round-trip time exceeds this value during one second, an ES will be indicated. Min: 0.001 ms. Max: 1000 ms. No default.
Jitter threshold (ms): Jitter threshold for triggering an errored second. If the jitter (delay variation) exceeds this value during one second, an ES will be indicated. Min: 0.001 ms. Max: 1000 ms. No default.
Note
Loss will always trigger an errored second.
Advanced¶
Collection interval (s): The interval at which results are collected from the Junos devices. Min: 5s Max: 300s Default: 5s.
Session timeout (s): The time after which idle sessions will be removed.
This functionality is offered in the Juniper API.
Filter control connection: Only collect results from the specified control connection as configured on the Junos device (irrespective of test session). Only one control connection can be specified. If you leave this blank, results will be collected from all control connections.
Filter test session: Only collect results from the specified test session as configured on the Junos device (irrespective of control connection). Only one test session can be specified. If you leave this blank, results will be collected from all test sessions.
If you filter on both control connection and test session, both of these must match.
Result metrics¶
RTT (ms): Delay between the transmission of a probe and the arrival of its response.
Egress jitter (ms): Difference between the current egress delay and the previous measurement.
Ingress jitter (ms): Difference between the current ingress delay and the previous measurement.
Round-trip jitter (ms): Difference between the current round-trip time and the previous measurement.
Egress interarrival jitter (ms): Estimate of the statistical variance of a packet’s interarrival time as defined in ► IETF RFC 1889, calculated for the outbound direction (from Junos device to reflector).
Ingress interarrival jitter (ms): Estimate of the statistical variance of a packet’s interarrival time as defined in IETF RFC 1889, calculated for the inbound direction (from reflector back to Junos device).
Round-trip interarrival jitter (ms): Estimate of the statistical variance of a packet’s interarrival time as defined in IETF RFC 1889, calculated for the full round-trip.
Note
Jitter and interarrival jitter are calculated differently from what is called “delay variation” in other tasks.
Loss (%): Round-trip packet loss in percent.
ES (s): Aggregated number of errored seconds (ES), taking into account all types of error.
ES loss (s): Number of errored seconds caused by loss.
ES RTT (s): Number of errored seconds caused by round-trip time.
ES jitter (s): Number of errored seconds for caused by jitter.